
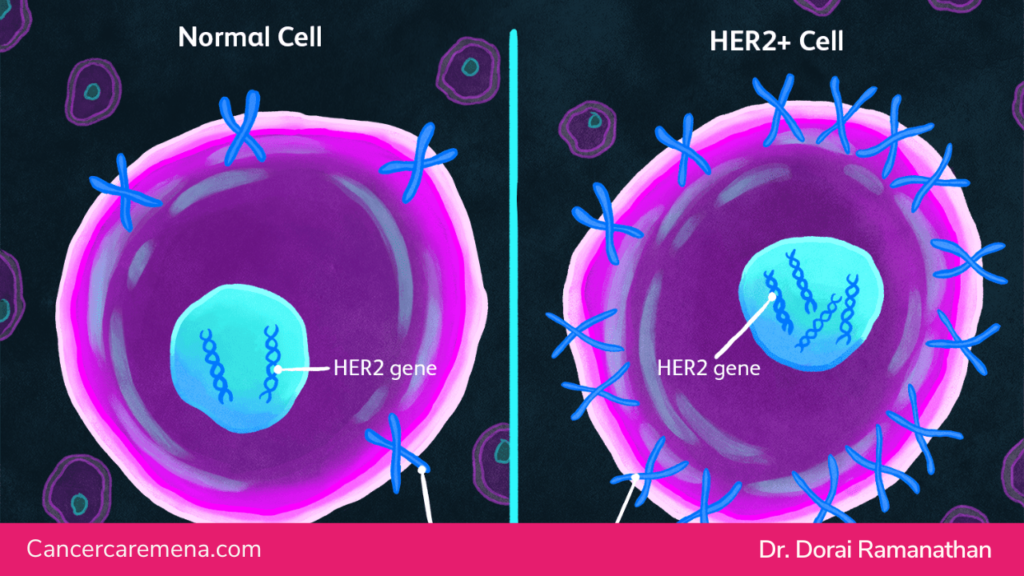
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease, and one of its aggressive subtypes is HER2-positive breast cancer. HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) is a protein that promotes the growth of cancer cells.
When breast cancer cells have overexpression or too many copies of the HER2 gene, they are classified as HER2-positive. This type of breast cancer tends to be more aggressive and has a higher risk of recurrence compared to other subtypes.
However, advances in medical research have led to the development of targeted therapies that specifically aim to inhibit the HER2 protein, revolutionizing the treatment landscape for HER2-positive breast cancer. In this blog, we will explore the key aspects of HER2-positive breast cancer, including its prevalence, diagnosis, treatment options, and targeted therapies.
Prevalence of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
HER2-positive breast cancer constitutes about 15-20% of all breast cancer cases. It is more commonly diagnosed in younger women and has a higher likelihood of affecting both breasts simultaneously.
Diagnosing HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the best treatment strategy. HER2 status is determined through HER2 testing, usually performed on the breast tissue obtained from a biopsy or surgery. The HER2 test helps categorize breast cancer as HER2-positive or HER2-negative.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for HER2-positive breast cancer depends on various factors, such as the stage of cancer, overall health, and individual preferences. Standard treatments may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy. However, targeted therapies have become a game-changer in treating HER2-positive breast cancer.
Targeted Therapies
HER2-targeted therapies are designed to specifically attack cancer cells that overexpress the HER2 protein, while sparing healthy cells. Some of the most effective targeted therapies include:
- Trastuzumab (Herceptin): An early success in HER2-targeted therapy, Herceptin has significantly improved the survival rates of HER2-positive breast cancer patients.
- Pertuzumab (Perjeta): Often combined with Herceptin, Pertuzumab has shown improved outcomes in both early-stage and metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer.
- Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla): This targeted therapy combines Herceptin with a chemotherapy drug, delivering a dual attack on HER2-positive cancer cells.
Evolving Research and Future Perspectives
Ongoing research is continually refining our understanding of HER2-positive breast cancer and its vulnerabilities. Clinical trials are exploring novel therapies and combinations to improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects. Personalized medicine approaches are also being investigated to tailor treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup and tumor characteristics.
In conclusion, understanding HER2-positive breast cancer is crucial for early detection and appropriate treatment. Targeted therapies have revolutionized the management of this aggressive breast cancer subtype, providing hope for improved outcomes and better quality of life for patients. Continued research and collaborative efforts among healthcare professionals hold the promise of further advancements, making HER2-positive breast cancer a manageable and ultimately curable condition.



